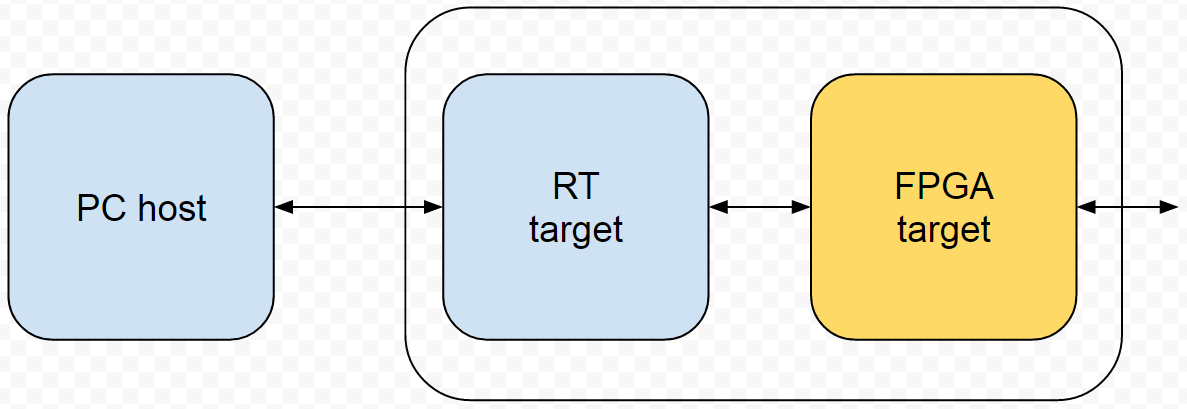
"FPGA" target
Develop an FPGA VI
FPGA guide
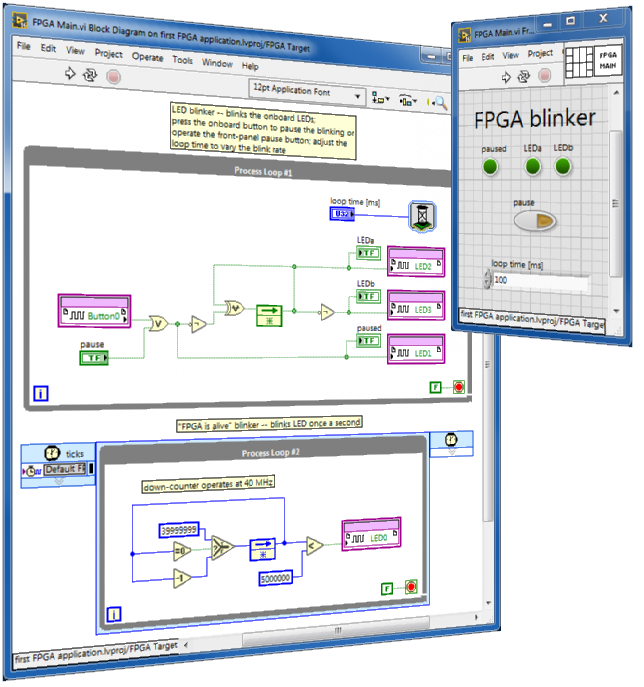
Make your first FPGA application
FPGA procedure
Create a new FPGA project
FPGA procedure
FPGA programming: Simulation techniques
FPGA guide PC guide
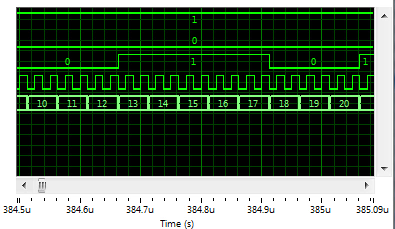
Simulate an FPGA VI
FPGA procedure
"Desktop Execution" node as an FPGA VI testbench
FPGA code PC code
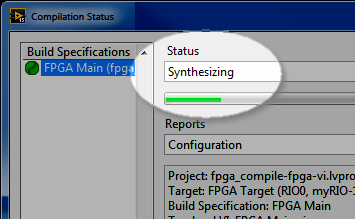
Compile an FPGA VI
FPGA procedure
Derived clock domains
FPGA code
FPGA programming: IP blocks
FPGA guide
Xilinx IP integration
FPGA code
Modify the default Academic RIO Device FPGA personality
FPGA procedure
Local variable (FPGA)
FPGA code
Global variable (FPGA)
FPGA code
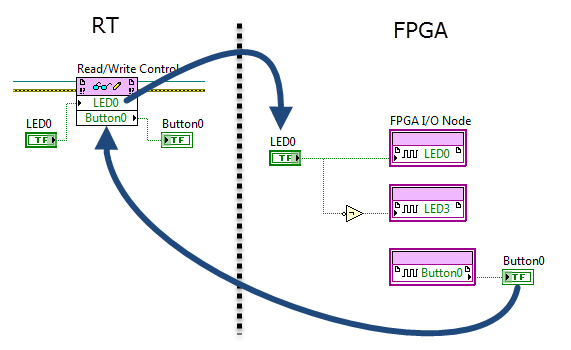
Programmatic front-panel communication with RT
FPGA code RT code
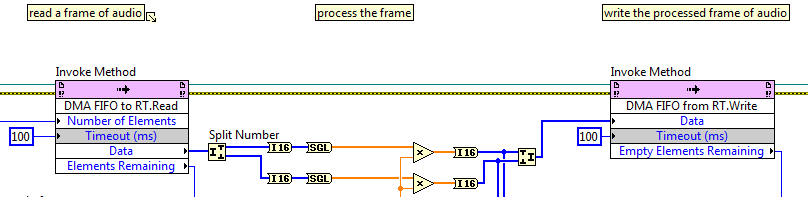
Stream high-speed data between FPGA and RT with a DMA FIFO
FPGA code RT code
Augmented default Academic RIO Device FPGA personality and high-precision waveform measurement application example
FPGA code RT code
FPGA/RT and FPGA/host inter-target communication
FPGA guide RT guide PC guide
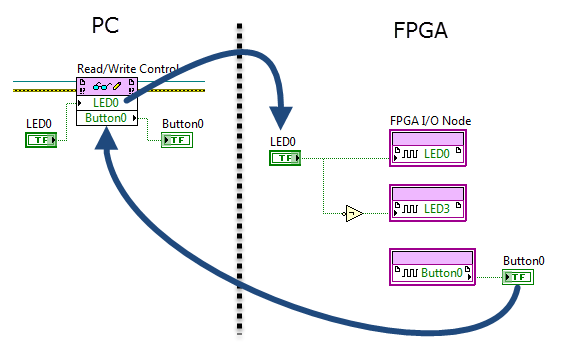
Programmatic front-panel communication with PC
FPGA code PC code
Stream high-speed data between FPGA and PC with a DMA FIFO
FPGA code PC code