RIO Developer Essentials Guide for Academia
"Network-published shared variable" tag
Make your first RT application
RT procedure
Follow along with this step-by-step tutorial to make a "hello, world!"-like application to experience the advantages of multiple linked VIs running simultaneously on the real-time (RT) target and desktop computer: (1) "RT Main" runs as the RT target start-up VI, blinks the onboard LEDs, and reads the onboard button; these onboard devices physically connect to the FPGA I/O pins which are accessed with the Academic RIO Device Toolkit Express VIs and default FPGA personality, and (2) "PC Main" VI runs on the desktop computer as a user-friendly human-machine interface (HMI) for remote command and control of "RT Main" through the network via shared variables hosted on the RT target.
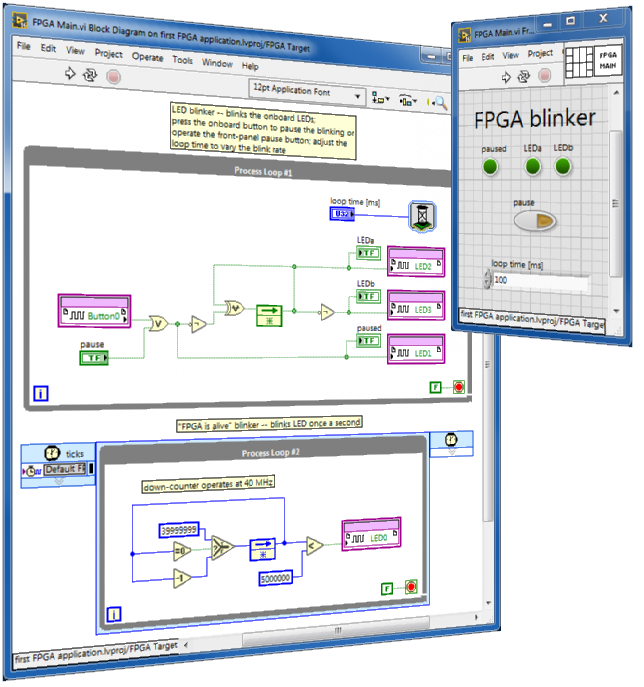
Make your first FPGA application
FPGA procedure
Follow along with this step-by-step tutorial to make a "hello, world!"-like application to experience the advantages of multiple linked VIs running simultaneously on the FPGA target, real-time (RT) target, and desktop computer: (1) "FPGA Main" VI blinks the onboard LEDs and reads the onboard button; these onboard devices physically connect to the FPGA I/O pins, (2) "FPGA testbench" VI runs on the desktop computer for interactive development and debugging of "FPGA Main" in simulation mode prior to compiling to a bitstream file, (3) "RT Main" VI runs as the RT target start-up VI; it runs "FPGA Main", interacts with its front-panel controls/indicators, and communicates with an external desktop computer via network-published shared variables, and (4) "PC Main" VI runs on the desktop computer as a user-friendly human-machine interface (HMI) for remote command and control of "FPGA Main" through the network.
A single-process shared variable (SPSV) behaves like a global variable that links deterministic and non-deterministic process loops, effectively shielding the deterministic loop from elements that contribute jitter.
RT procedures: Network-published shared variables (NPSVs)
RT guide PC guide
An NPSV behaves like a global variable to connect the RT target and PC host through a network.
Create a network-published shared variable (NPSV)
RT procedure PC procedure
The network-published shared variable (NPSV) behaves like a global variable to link targets through the network.
Bind a PC VI front-panel indicator to a network-published shared variable (NPSV)
RT procedure PC procedure
A quick and easy way for a PC HMI (human-machine interface) VI to observe the state of an RT-hosted network-published shared variable (NPSV) without creating any block diagram code; an alternative to programmatically accessing the NPSV value.
Network-published shared variable (NPSV)
RT code PC code
A network-published shared variable (NPSV) behaves like a global variable that links process loops residing in two or more network-connected targets.
Use the NPSV programmatic API (application programmer's interface) VIs as an alternative method to a shared variable node.
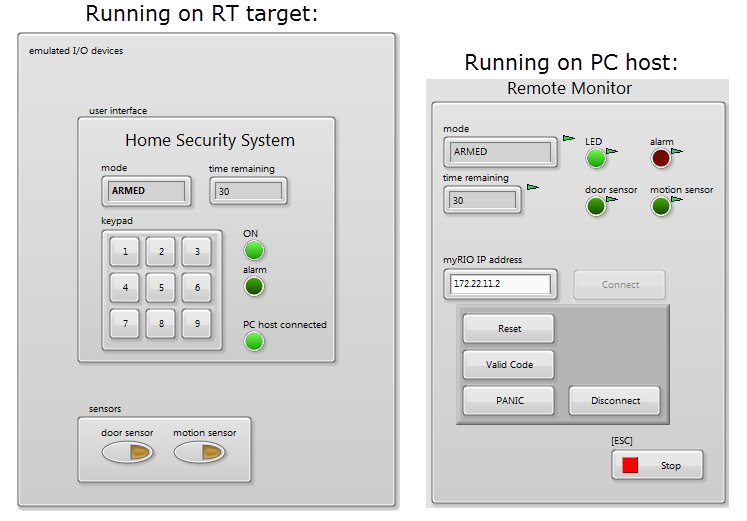
System controller application example: Home Security System
RT code PC code
Example of a complete RT system controller based on the Queued Message Handler (QMH) design pattern with multiple parallel task loops implementing behaviors with queued state machines (QSMs), various inter-process communication techniques (queues and local variables), and inter-target communication techniques (network-published shared variables (NPSVs) and network streams). The PC host human-machine interface (HMI) can remotely connect to the system through the network, monitor the status of the security system, and control it remotely.