RIO Developer Essentials Guide for Academia
"Event Structure" element

Make your first RT application
RT procedure
Follow along with this step-by-step tutorial to make a "hello, world!"-like application to experience the advantages of multiple linked VIs running simultaneously on the real-time (RT) target and desktop computer: (1) "RT Main" runs as the RT target start-up VI, blinks the onboard LEDs, and reads the onboard button; these onboard devices physically connect to the FPGA I/O pins which are accessed with the Academic RIO Device Toolkit Express VIs and default FPGA personality, and (2) "PC Main" VI runs on the desktop computer as a user-friendly human-machine interface (HMI) for remote command and control of "RT Main" through the network via shared variables hosted on the RT target.
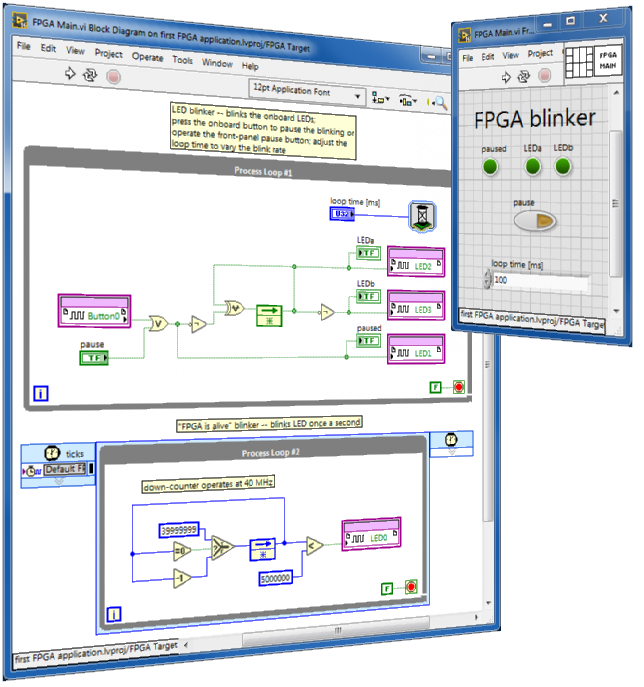
Make your first FPGA application
FPGA procedure
Follow along with this step-by-step tutorial to make a "hello, world!"-like application to experience the advantages of multiple linked VIs running simultaneously on the FPGA target, real-time (RT) target, and desktop computer: (1) "FPGA Main" VI blinks the onboard LEDs and reads the onboard button; these onboard devices physically connect to the FPGA I/O pins, (2) "FPGA testbench" VI runs on the desktop computer for interactive development and debugging of "FPGA Main" in simulation mode prior to compiling to a bitstream file, (3) "RT Main" VI runs as the RT target start-up VI; it runs "FPGA Main", interacts with its front-panel controls/indicators, and communicates with an external desktop computer via network-published shared variables, and (4) "PC Main" VI runs on the desktop computer as a user-friendly human-machine interface (HMI) for remote command and control of "FPGA Main" through the network.
Send messages through a network stream channel
RT code PC code
Send command and status messages through a low-latency lossless network-based data communication channel between the RT target and PC host system.
Create a responsive user interface based on two loops operating in parallel: the "producer" loop event structure responds immediately to user interactions such as button clicks and mouse movements that send commands through a queue to the "consumer" loop which performs the required tasks. Separating the state machine into two loops allows the user interface to remain responsive should a consumer task require an unusual amount of time or must wait for a shared resource to become available.
TCP client-server
RT code PC code
Create a server on the Academic RIO Device that listens for TCP/IP network connection requests from a client running on the PC host, accepts client information including the desired state of the four onboard LEDs, sets the LEDs accordingly, and returns the state of the onboard 3-axis accelerometer and pushbutton.
UDP client-server
RT code PC code
Create a server on the Academic RIO Device that listens for UDP datagram messages from a client running on the PC host, accepts client information including the desired state of the four onboard LEDs, sets the LEDs accordingly, and returns the state of the onboard 3-axis accelerometer and pushbutton.